Simulador Weaver on-line
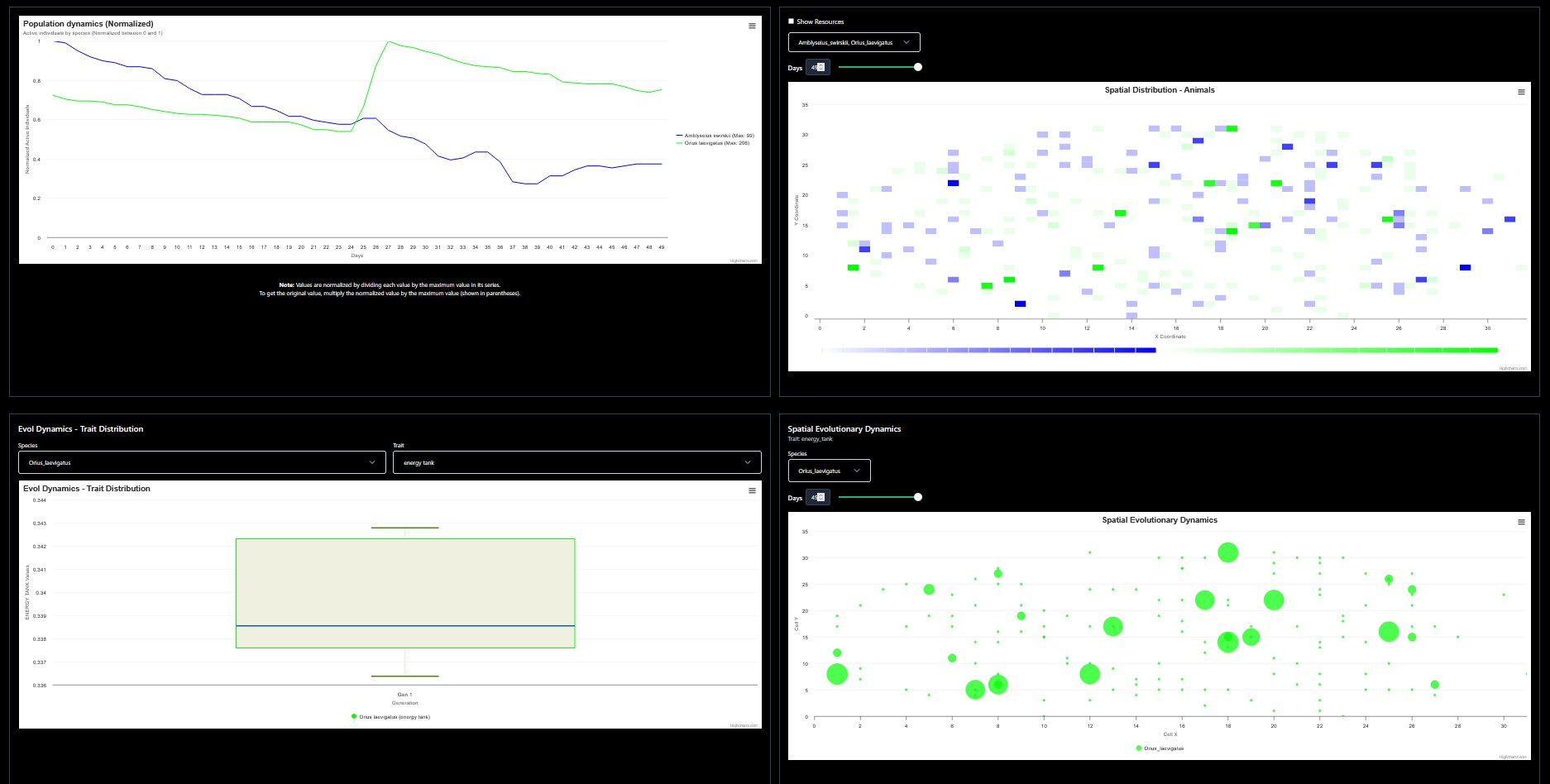
This is a running example (parameterized by E. Fenoy, D. Quevedo and J. Moya-Laraño) of a predator and prey food web module, in which the predator has access to alternative prey and is able to dynamically switch preferences between the focal and alternative prey depending on their relative abundances. When the possibility of flexible behavior to dynamically specialize on the more abundant prey is turned off (slider), the focal prey goes to extinction early on from predator overexploitation.
If run long enough, the dynamics is persistent through 10,000 days (37 generations for the predator and 226 for the prey). This persistent food web module was found using a tri-objective genetic algorithm (written by M. Carmona) and sweeping over 33 parameters. We optimized dynamics over 1000 days and then run the winner simulation for 10,000 days. The result shows that as in the wild, the predator has one generation per year, and the prey has several through the entire season. This is but a preliminary demo of Weaver capabilities, we will be updating this page with more examples and case studies.
Upper-left panel: population dynamics (relative numbers, 0-1 scaled for better visualization of relative abundances).
Upper-right panel: spatial dynamics (abundances are relative for better visualization)
Bottom-left panel: evolutionary dynamics of given traits (standardized N|0,1|).
Bottom-right panel: trait evolutionary spatial dynamics.
Dirección
Addres Att. Jordi Moya-Laraño, Estación Experimental de Zonas Áridas, EEZA-CSIC, Carretera de Sacramento, 04120-Almería Spain

